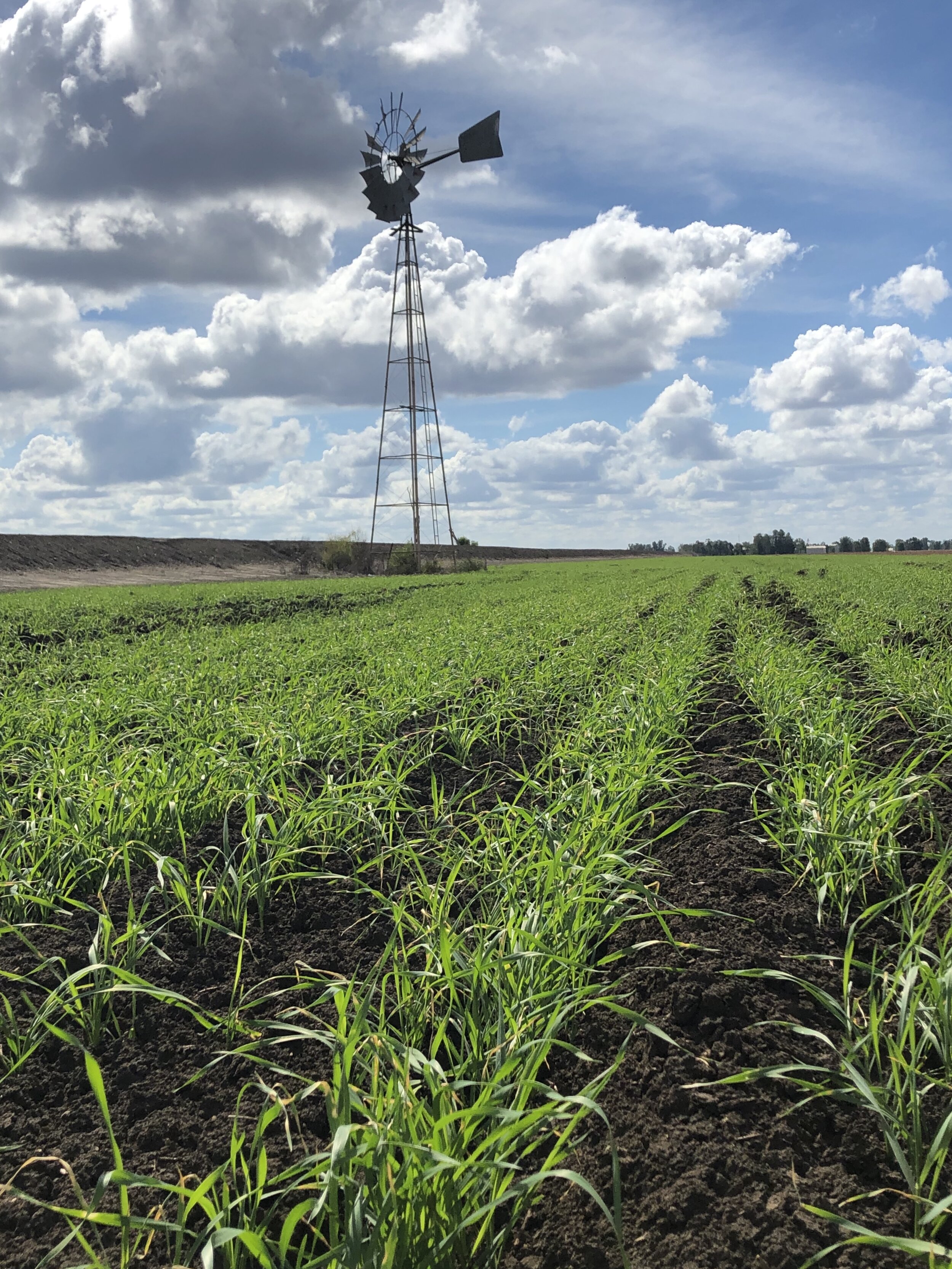
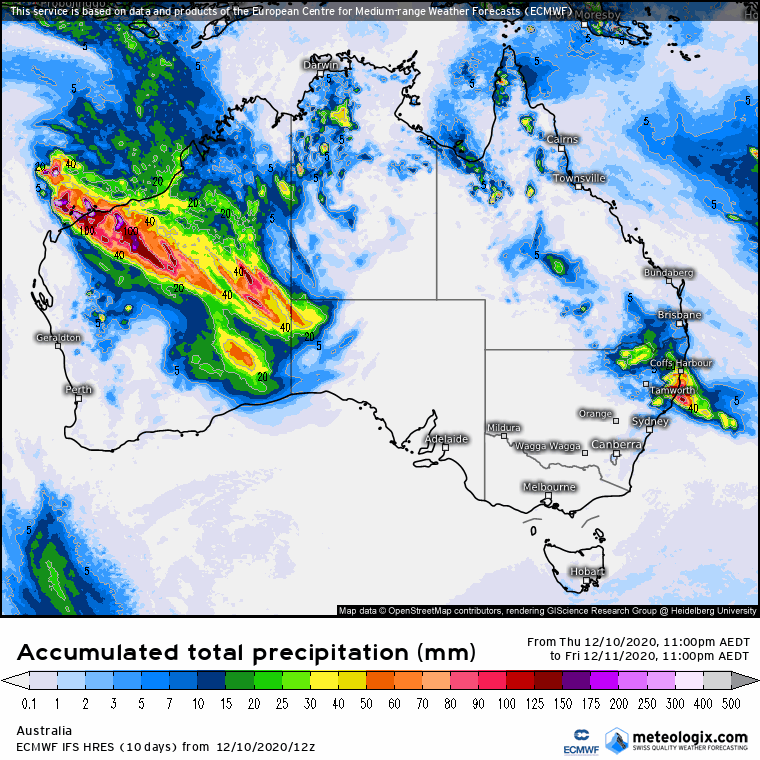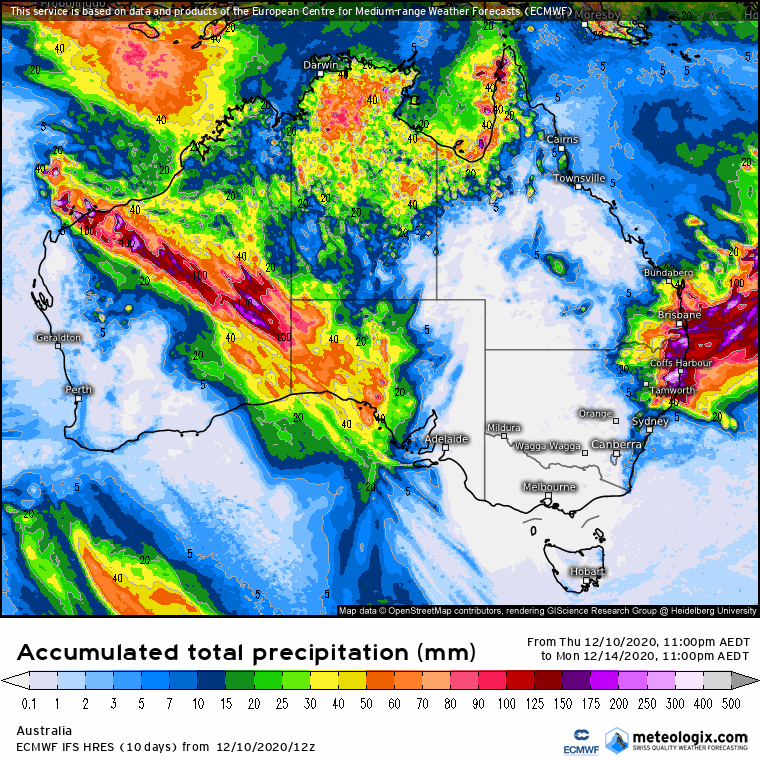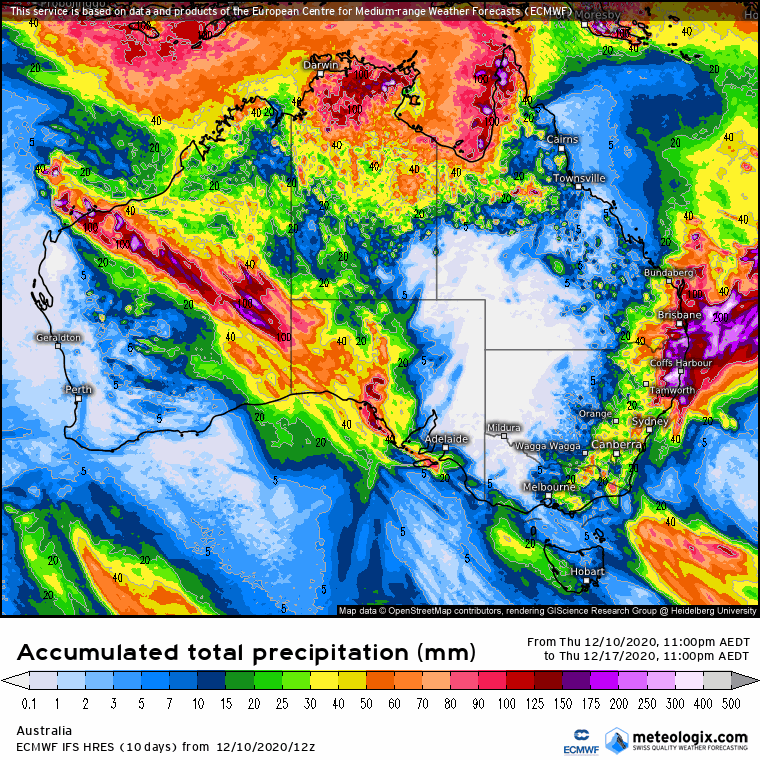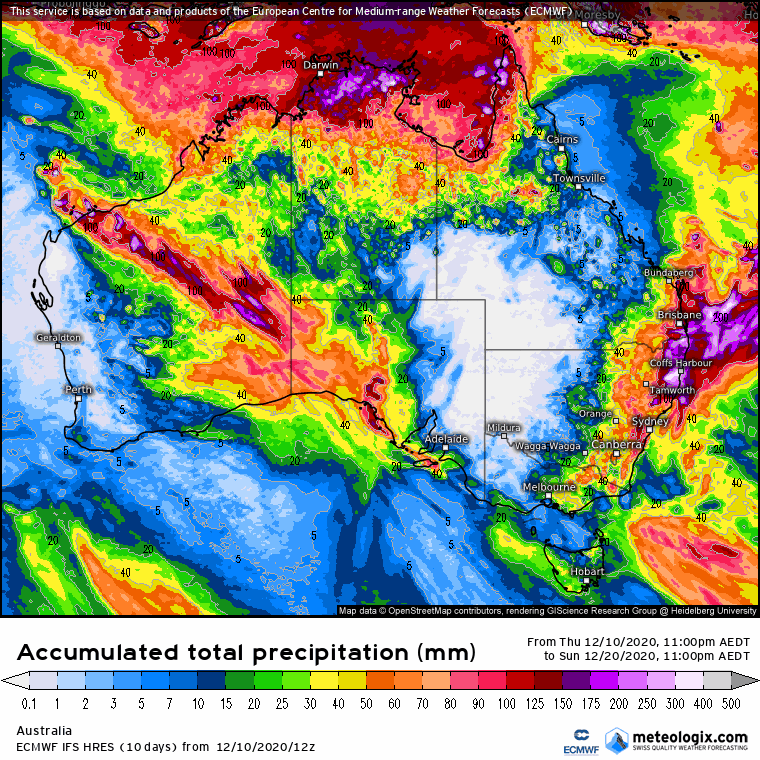
The Southern Annular Mode (SAM) index has finally broken through into positive phase over the last week, which could affect weather patterns in eastern Australia during the coming months.
The SAM is an index that measures the north-south displacement of a band of westerly winds flowing between Australia and Antarctica.
When the SAM index is negative, these westerly winds move towards Australia and when it is positive, they contract towards Antarctica.
The positive phase of the SAM is linked to the stratospheric cooling over Antarctica, which made headlines last year for extreme warming (Left graph) relating to a negative SAM, not seen since the horrible drought year of 2002. The circle showed “çoupling” with the troposphere, which is where the SAM is measured and consequently, spent the rest of the year in a negative phase.
The second image (Right graph) shows the current - and very opposite situation. Stratospheric cooling has just “coupled” with the SAM, showing the cooling (blue) colours right through different heights of the atmosphere.
What does this mean? Stratospheric cooling (or warming) was found by Hendon et al (2020) to have a connection with the SAM. It’s anticipated that the SAM will be positive during La Niña, but this analysis does provide added confidence. A positive SAM occurs when the winds in the southern ocean contract (last image), allowing more tropical moisture to move south into the mid-latitudes increasing the chance of late spring and summer rain. SAM moving back into positive territory is a good sign for rainfall on summer pastures and crops from NSW through to the northern Darling Downs.
Want to learn more about SAM - watch this 2 minute youTube video